14) Review Cyclic Structure of Glucose and Linkages in Starch Glycogen
Students of class 12 Chemistry should refer to MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemical science Biomolecules with answers provided hither which is an of import affiliate in Class 12 Chemical science NCERT textbook. These MCQ for Class 12 Chemistry with Answers have been prepared based on the latest CBSE and NCERT syllabus and examination guidelines for Course 12 Chemistry. The post-obit MCQs tin help you to do and get ameliorate marks in the upcoming class 12 Chemistry exam
Chapter 14 Biomolecules MCQ with Answers Form 12 Chemistry
MCQ Questions Class 12 Chemistry Biomolecules provided below have been prepared by expert teachers of grade 12. These objective questions with solutions are expected to come in the upcoming Standard 12 examinations. Learn the below provided MCQ questions to get better marks in examinations.
Question. Which one of the post-obit compounds is establish abudnantly in nature?
(a) Fructose
(b) Starch
(c) Glucose
(d) Cellulose
Question. A carbohydrate that cannot exist hydrolysed into simpler units is called
(a) polysaccharides
(b) trisaccharides
(c) disachharides
(d) monosaccharides
Question. 3 cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below which of these are anomers.
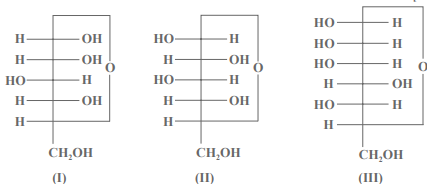
(a) I and Ii
(b) II and III
(c) I and III
(d) III is anomer of I and Ii
Question. Which amid the following is the simplest sugar?
(a) Glucose
(b) Starch
(c) Cellulose
(d) None of these
Question. Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
(a) It is an aldohexose.
(b) On heating with Hullo it forms n-hexane.
(c) It is nowadays in furanose grade.
(d) It does not give 2,4-DNP exam.
Question. Which of the post-obit is a disaccharide ?
(a) Lactose
(b) Starch
(c) Cellulose
(d) Fructose
Question. The sugar that is characteristic of milk is
(a) maltose
(b) ribose
(c) lactose
(d) galactose
Question. Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have
D configuration.
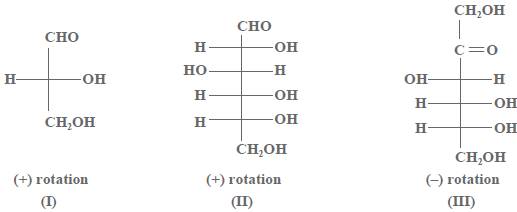
(a) I, Two, III
(b) 2, III
(c) I, II
(d) Three
Question. Which of the following reactions of glucose tin exist explained but by its cyclic structure?
(a) Glucose forms pentaacetate.
(b) Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime.
(c) Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
(d) Glucose is oxidised by nitric acrid to gluconic acid.
Question. Which of the following reaction confirms the presence of carbonyl group (> C—O) in glucose?
(a) Reaction with HI
(b) Reaction with hydroxylamine
(c) Reaction with HCN
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question. DNA and RNA incorporate iv bases each. Which of the post-obit bases is not nowadays in RNA?
(a) Adenine
(b) Uracil
(c) Thymine
(d) Cytosine
Question. The presence or absence of hydroxyl group on which carbon cantlet of carbohydrate differentiate RNA and Deoxyribonucleic acid
(a) 2d
(b) 4th
(c) 3rd
(d) 1st
Question. Fructose reduces Tollens' reagent due to
(a) Primary alcoholic group
(b) Asymmetric carbons
(c) Secondary alcoholic groups
(d) Enolisation of fructose followed by conversion to aldehyde past base
Question. Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis and also as reducing or non-reducing carbohydrate. Sucrose is a __________.
(a) monosaccharide
(b) disaccharide
(c) reducing sugar
(d) non-reducing carbohydrate
Question. Milk changes afterwards digestion into
(a) cellulose
(b) fructose
(c) glucose
(d) lactose
Question. Which one of the following is an ester ?
(a) Coconut o il
(b) Kerosene oil
(c) Lather
(d) Glycerine
Question. Which of the following does non form an oxime?
(a) Glucose
(b) Glucose pentaacetate
(c) Arabi nose
(d) Galactose
Question. Vitamin Bhalf dozen is known as
(a) Pyridoxin
(b) Thiamine
(c) Tocopherol
(d) Riboflavin
Question. Glucose molecule reacts with 'X' number of molecules of phenyl hydrazine to yield osazone. The value of 'Ten' is
(a) iv
(b) one
(c) two
(d) three
Question. Which set of terms correctly identifies the carbohydrate shown?

I. Pentose
II. Hexose
Three. Aldose
Iv. Ketose
V. Pyranose
6. Furanose
(a) I, III and VI
(b) I, III and V
(c) 2, Iii and V
(d) Two, 3 and 6
(e) l, 4 and VI
Question. Diabetes is detected, using . . . . . . for testing mine of patients.
(a) Fehling's solution
(b) Tollen's reagent
(c) Benedict's solution
(d) Baeyer's reagent
Question. The anomeric carbon in D(+) glucose is
(a) C-one carbon
(b) C-2 carbon
(c) C-5 carbon
(d) C-6 carbon
Question. Glucose contains in addition to aldehyde group
(a) 1 secondary OH and four main OH groups
(b) i primary OH and four secondary OH groups
(c) two primary OH and three secondary OH groups
(d) 3 primary OH and two secondary OH groups
Question. Which of the post-obit indicates open chain construction of glucose?
(a) Pentaacetyl derivative of glucose
(b) Cyanohydrin formation with HCN
(c) Reaction with Fehling's solution
(d) Reaction with Tollen's reagent
Question. Complete hydrolysis of cellulose gives
(a) D-fructose
(b) D-ribose
(c) D-glucose
(d) L-glucose
Question. Which one of the following is an case of a not-reducing saccharide?
(a) Sucrose
(b) Lactose
(c) Maltose
(d) Cellobiose
Question. Methyl α-D-glucoside and methyl- β-D-glucoside are
(a) epimers
(b) anomers
(c) enantiomers
(d) conformational diastereomers
Question. Iodine examination is shown by
(a) glucose
(b) starch
(c) glycogen
(d) polypeptide
Question. Raffinose is
(a) trisaccharide
(b) disaccharide
(c) monosaccharide
(d) polysaccharide
Question. Glucose is a/an
(a) polyhydroxy ketone
(b) alcohol
(c) hydrate of carbon
(d) pentahydroxy aldehyde
Question. All monosaccharides …… Tollen's reagent.
(a) oxidises
(b) condense with
(c) reduces
(d) add to
Question. Cellulose is a polymer of
(a) glucose
(b) fructose
(c) ribose
(d) sucrose
Question. Lactose gives on hydrolysis
(a) glucose
(b) glucose and galactose
(c) fructose
(d) glucose and fructose
Question. Number of chiral carbon atoms in β-D-(+)- glucose is
(a) 5
(b) six
(c) three
(d) four
Question. Sucrose on hydrolysis gives
(a) glucose and maltose
(b) glucose and lactose
(c) glucose and fructose
(d) but glucose
Question. The two functional groups present in a typical carbohydrate are:
(a) – CHO and – COOH
(b) > C = O and – OH
(c) – OH and – CHO
(d) – OH and – COOH
Question. Which of the following pairs represents anomers?

Question. The reaction of glucose with red P + How-do-you-do is called
(a) Sandmeyer'south reaction
(b) Reformatsky reaction
(c) Gattermann's reaction
(d) Reduction
Question. Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained but past its cyclic structure?
(a) Glucose forms pentaacetate
(b) Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to class an oxime
(c) Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine
(d) Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid
Question. Amylopectin is insoluble in water and constitutes about
(a) xv–20% of starch
(b) twenty–40% of starch
(c) 50–seventy% of starch
(d) lxxx–85% of starch
Question. Cellulose is not digestible by human beings due to absenteeism of cellulose hydrolysing enzyme called
(a) cellulase
(b) invertase
(c) zymase
(d) urease
Question. Glycogen is a branched chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1—C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1—C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is like to __________.
(a) Amylose
(b) Amylopectin
(c) Cellulose
(d) Glucose
Question. Which of the following polymer is stored in the liver of animals?
(a) Amylose
(b) Cellulose
(c) Amylopectin
(d) Glycogen
Question. Which of the following naturally occurring a– aminoacids is optically inactive?
(a) Glycine
(b) Alanine
(c) Leucine
(d) Valine
Question. Each polypeptide in a protein has aminoacids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be __________.
(a) primary structure of proteins.
(b) secondary structure of proteins.
(c) tertiary construction of proteins.
(d) quaternary structure of proteins.
Question. Maltose and glucose are
(a) oxidising carbohydrate
(b) reducing sugar
(c) kickoff is oxidising and 2nd is reducing saccharide
(d) both are non-reducing sugar
Question. Proteins are found to have two unlike types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sail structure. α-helix construction of protein is stabilised by :
(a) Peptide bonds
(b) van der Waals forces
(c) Hydrogen bonds
(d) Dipole-dipole interactions
Question. Nucleic acids are the polymers of __________.
(a) nucleosides
(b) nucleotides
(c) bases
(d) sugars
Question. Glucose gives silver mirror test with Tollen's reagent. It shows the presence of
(a) acidic grouping
(b) alcoholic group
(c) ketonic group
(d) aldehyde group
Question. The symbols D and Fifty represents
(a) the optical action of compounds.
(b) the relative configuration of a particular stereoisomer.
(c) the dextrorotatory nature of molecule.
(d) the levorotatory nature of molecule
Question. Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
(a) 5′ and 3′
(b) 1′ and 5′
(c) 5′ and 5′
(d) 3′ and iii′
Question. Proteins can be classified into 2 types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are :
(a) Insulin
(b) Keratin
(c) Albumin
(d) Myosin
Question. Which ane of the post-obit compounds is different from the residual?
(a) Sucrose
(b) Maltose
(c) Lactose
(d) Glucose
Question. Which of the following reagent cannot distinguish between glucose and fructose?
(a) Fehling's solution
(b) Tollen's reagent
(c) Benedict'due south solution
(d) All of these
Question. Which one of the post-obit does not exhibit the phenomenon of mutarotation ?
(a) (+) – Sucrose
(b) (+) – Lactose
(c) (+) – Maltose
(d) (–) – Fructose
Question. Glucose tin can't be classified as
(a) hexose
(b) carbohydrate
(c) aldose
(d) oligosaccharide
Question. The function of glucose is to
(a) provides free energy
(b) promote growth
(c) prevent diseases
(d) perform all above
Question. Which of the following is the sweetest sugar?
(a) Sucrose
(b) Glucose
(c) Fructose
(d) Maltose
Question. Select the uses of carbohydrates.
(a) Honey is used equally instant source of energy by vaids in ayurvedic arrangement of medicine
(b) These are used as storage molecules
(c) They are used in furniture, cotton fibre, lacquers
(d) All of the above
Question. Deoxyribonucleic acid multiplication is called as
(a) translation
(b) transduction
(c) transcription
(d) replication
Question. Chromosomes are fabricated from
(a) proteins
(b) nucleic acids
(c) proteins and nucleic acids
(d) carbohydrates and nucleic acids
Question. Cellulose is a polymer of
(a) Glucose
(b) Fructose
(c) Ribose
(d) Sucrose
Question. Which of the following is likewise known as fauna starch?
(a) Glycine
(b) Glycogen
(c) Amylose
(d) Cellulose
Question. Which of the post-obit B group vitamins can be stored in our body?
(a) Vitamin Bane
(b) Vitamin Bii
(c) Vitamin B6
(d) Vitamin B12
Question. Which of the following acids is a vitamin?
(a) Aspartic acrid
(b) Ascorbic acid
(c) Adipic acid
(d) Saccharic acid
Question. The double helical construction of DNA was proposed by
(a) Watson and Crick
(b) Meichers
(c) Emil Fischer
(d) Khorana
Question. Which one is the complementary base of cytosine in one strand to that in other strand of Deoxyribonucleic acid?
(a) Adenine
(b) Guanine
(c) Thymine
(d) Uracil
Question. Biomolecules are
(a) aldehydes and ketones
(b) acids and esters
(c) carbohydrates, proteins and fats
(d) alcohols and phenols
Question. Sucrose on hydrolysis gives
(a) fructose+ribose
(b) glucose + fructose
(c) glucose+glucose
(d) fructose + fructose
Question. Invert sugar is
(a) chemically inactive form of saccharide
(b) equimolecular mixture of glucose and fructose
(c) mixture of glucose and sucrose
(d) a variety of cane sugar

Nosotros hope the above multiple option questions for Class 12 Chemistry for Affiliate 14 Biomolecules provided above with answers based on the latest syllabus and exam guidelines issued by CBSE, NCERT and KVS are really useful for you. Biomolecules is an important chapter in Class 12 as it provides very potent agreement well-nigh this topic. Students should get through the answers provided for the MCQs subsequently they take themselves solved the questions. All MCQs have been provided with four options for the students to solve. These questions are really useful for benefit of class 12 students. Please become through these and let us know if you accept whatsoever feedback in the comments section.
Source: https://dkgoelsolutions.com/mcqs-for-chemistry-class-12-with-answers-chapter-14-biomolecules/
0 Response to "14) Review Cyclic Structure of Glucose and Linkages in Starch Glycogen"
Post a Comment